Atmosphere: Jupiter’s atmosphere is very like the Suns’. For
instance, it is made up of mostly Hydrogen and Helium. Further into Jupiter’s
atmosphere, the hydrogen gas is turned into a liquid due to increased
temperature and pressure. Then, further in, the hydrogen changes into a
metallic substance and is able to conduct electricity.
Water exists deep
within Jupiter’s atmosphere. Jupiter has a very strong magnetic field due to its
quick rotation. Jupiter possesses a magnetic field 20,000 times stronger than
the Earth’s. Many of the moons circling the planet Jupiter may in fact be asteroids
caught inside the planet’s strong magnetic field. Jupiter also has a huge gravitational force about 2.5 times that of Earth's.
Jupiter and its belts and zones
Surface features: Jupiter has many light and dark coloured
stripes, or bands. The dark bands are called belts and the light bands, light
zones. Storms have raged around these belts and zones for hundreds of years.
Internal Structure of
Jupiter: Jupiter’s core is
thought to be made of a solid ice-rock about the size of Earth. Around this there
is predicted to be a layer of liquid metallic hydrogen. The outer layer of
Jupiter is made up of mainly hydrogen.
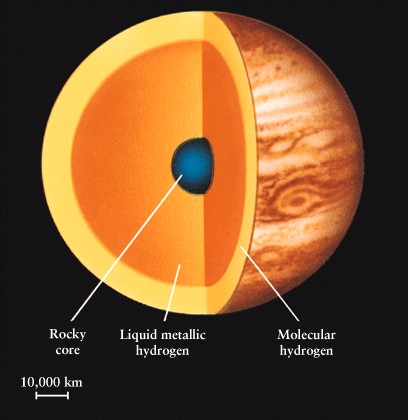
The internal structure of Jupiter

The internal structure of Jupiter
Temperature: An average temperature of -148 ºC
Weather conditions: There are strong East-west winds in a zone, and
west to east winds in a belt. Wind speeds are around 360km/h in zones. Jupiter
has many storm clouds, which are mainly made up of ammonia. Jupiter often
experiences lightning storms due to its extremely strong magnetic field, which
traps a collection of charged particles, ions, electrons and radiation.
Lightning is also
present on Jupiter; sometimes reflects off the storm clouds, making Jupiter
becomes clearly visible at times. There are two layers of storm clouds around
Jupiter: a thick layer and a thin layer.
Jupiter is a gas
giant, and is made of hydrogen. Large pressure and high temperatures can cause
this hydrogen to become a liquid metal, which has then been solidified into its
metal form using large pressure and at a temperature of 14 kelvin (-259.15 ºC) so that humans can stand on it.
Since Jupiter’s normal
magnetoscope (magnetic field around Jupiter) has a level of radiation that is
1,000 times the deadly level for a human, the radiation level has also had to
be severally altered in order to allow humans to travel there.
Don't worry though, everything is safe and has been tested many times.
Don't worry though, everything is safe and has been tested many times.





